- your liver may be working harder than usual
- you may not be able to store as many nutrients as usual
The information on this page can help you get the nutrition (protein, calories, vitamins, and minerals) you need to stay strong and be able to do the things you need to do every day. It will also help you cut down on the salt (sodium) you eat.
When to Eat
Some people with cirrhosis can find eating quite challenging. Lack of hunger, fluid build-up, and nausea are just some examples of things that may impact your ability to eat. You can improve your food intact by making sure you eat:
- breakfast soon after you wake up
- every 3 to 4 hours during the day
- a snack before bed, and again if you wake in the night
Protein
Everyone needs a different amount of protein. Talk to your healthcare provider about how much is right for you. Start by eating 3 meals and 2–3 snacks each day. Have a bedtime snack every day
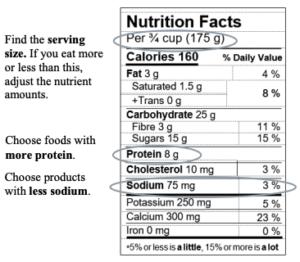
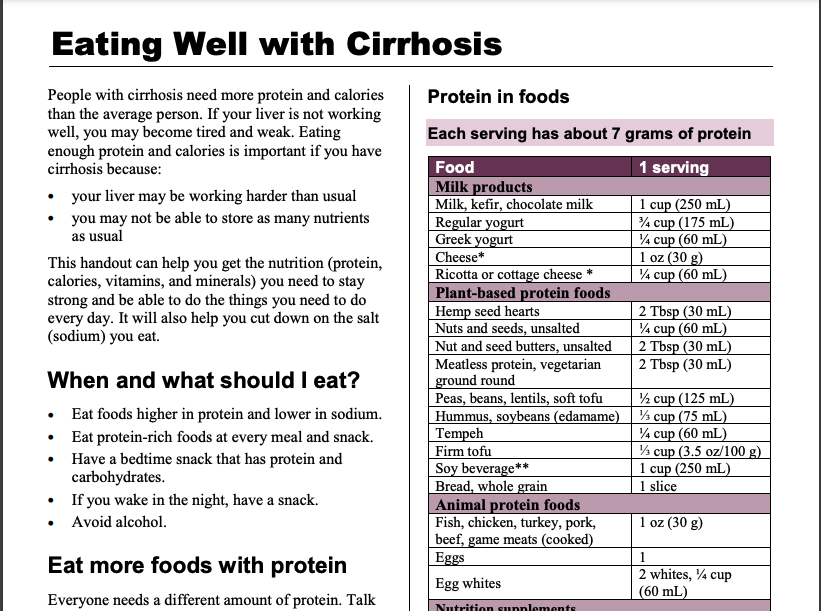
Protein in foods
Use the Protein in foods table below to choose:
- at least 2–3 servings of protein at each meal, and
- at least 1–2 servings of protein at each snack.
| Food | 1 serving |
|---|---|
| Milk products | |
| Milk, kefir, chocolate milk | 1 cup (250 mL) |
| Regular yogurt | 3/4 cup (175 mL) |
| Greek yogurt | 1/4 cup (60 mL) |
| Cheese * | 1 0z (30g) |
| Ricotta or cottage cheese* | 1/4 cup (60 mL) |
| Plant-based protein foods | |
| Hemp seed hearts | 2 Tbsp (30 mL) |
| Nuts and seeds, unsalted | 1/4 cup (60 mL) |
| Nut and seed butters, unsalted | 2 Tbsp (30 mL) |
| Meatless protein, vegetarian ground round | 2 Tbsp (30 mL) |
| Peas, beans, lentils, soft tofu | 1/2 cup (125 mL) |
| Hummus, soybeans (edamame) | 1/3 cup (75 mL) |
| Tempeh | 1/4 cup (60 mL) |
| Firm tofu | 1/3 cup (3.5 oz/100g) |
| Soy beverage** | 1 cup (250 mL) |
| Bread, whole grain | 1 slice |
| Animal protein foods | |
| Fish, chicken turkey, pork, beef, game meats (cooked) | 1 oz (30 g) |
| Eggs | 1 |
| Egg whites | 2 whites, 1/4 cup (60 mL) |
| Nutrition supplements | |
| Nutrition supplement drinks, bars, pudding Protein powders Protein bars, shakes |
Protein amounts vary. Read nutrition Facts tables on packages. |
Meals higher in protein
- Add beans or lentils to soups, stews, and sauces.
- Melt low salt cheese in soups, sauces, scrambled eggs, and casseroles.
- Have cereal with 1 cup of milk at breakfast.
Snacks higher in protein
- Add protein powder to hot cereal, smoothies, pudding, and homemade muffins.
- Add unsalted nuts, seeds, and wheat germ to cereals, salads, smoothies, or yogurt.
- Toast with 2 Tbsp (30 mL) peanut butter.
- A muffin with cheese
- Fruit and a container of Greek yogurt
- A smoothie: banana, milk, protein powder.
- Have a nutrition supplement drink.
Talk to your healthcare team about other ways to increase the protein in your diet.
Take a look at this handout for more information about protein and cirrhosis: Eating well with cirrhosis
Sodium (Salt)
Too much sodium can make your body hold on to extra fluid. This fluid can pool in your belly and legs. Swelling in your belly (ascites) can make you feel fuller, quicker. Eating foods with less sodium can help control ascites.
- Aim to eat less than 2000 mg of sodium a day.
- One teaspoon of salt has about 2300 mg of sodium.
- All types of salt contain the same amount of sodium, including table salt, sea salt, and Himalayan salt.
Tips to reduce sodium:
- At first, foods may taste bland. Over time, your taste buds get used to less salt.
- Don’t add salt to your food while cooking or at the table.
- Choose fresh, unprocessed, and homemade foods.
- Eat less processed, packaged, or restaurant foods.
- Limit condiments and sauces (ketchup, mustard, soy sauce, gravies, salad dressings).
- Limit pickled foods, olives, chutneys, and dips.
- To boost flavours, try adding spices, seasoning mixes with no salt added, lemon, lime, vinegar, fresh or dry herbs, garlic, or onions
Learn to read food labels
Vitamins and Supplements
People with cirrhosis can be low in some vitamins and minerals. Osteoporosis (weak bones) is common in liver disease. Getting enough vitamin D and calcium will help keep your bones strong.
- Every day, take a multivitamin and mineral pill with no iron.
- You may be asked to take calcium or vitamin D pills.
- Talk to your healthcare team about what kind of supplement is right for you
- There are many complementary and alternative medicines that are available that claim to ease the symptoms of liver disease or to reduce your risk of developing liver disease. Most of these medicines are processed by the liver, and can be very dangerous to people with liver problems. To learn more about these medicines, Click Here.
The Importance of Nutrition to Prevent and Treat Low Muscle Mass
The Nutrition in Cirrhosis Guide
 Our national team of healthcare practitioners specializing in cirrhosis developed a practical “nutrition tool” for patients. With our patients, this became “The Nutrition in Cirrhosis Guide” – intended for patients as well as their family and friends.
Our national team of healthcare practitioners specializing in cirrhosis developed a practical “nutrition tool” for patients. With our patients, this became “The Nutrition in Cirrhosis Guide” – intended for patients as well as their family and friends.
For personalized nutrition assistance, ask your doctor or get a referral to a registered dietitian. Both types of healthcare practitioners can provide personalized nutrition goals and help you reach them.
To download the complete “Nutrition in Cirrhosis Guide” (40 pages) as a .pdf file, click here.
The Guide was made possible from extensive feedback from patients, and their family & friends, who attend The Cirrhosis Care Clinic (TCCC) at the University of Alberta in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada.
Funding for the Guide’s creation was obtained from a research grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) and Alberta Innovates. Alberta Health Services provided protected time to V DenHeyer.

The following organizations provided support in the form of unrestricted educational grants to support the Guide:

Peer review regarding the content and format of the Guide was obtained from registered dietitians (RDs) and gastroenterologists in Halifax, Montreal, Toronto, Edmonton, Calgary, and Vancouver. Additional input was obtained from experts across North America and Europe. Thank you for your valuable input and assistance.
If any portion of the Guide is used in research, communications, or patient care, please use the following citation:
Tandon P, DenHeyer V, Ismond KP, Kowalczewski J, Raman M, Eslamparast T, Bémeur C, Rose C. The Nutrition in Cirrhosis Guide. University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta. 2018. pp. 1- 40.
The Nutrition in Cirrhosis Guide may be reproduced for non-commercial use as is and in its entirety without further permission. Adaptations, modifications, unofficial translations, and/or commercial use of The Nutrition in Cirrhosis Guide are strictly prohibited without prior permission.
This chapter covers the following topics:
-
What is malnutrition?
-
Warning signs of malnutrition
-
Who is at-risk for malnutrition?
-
Why are patients with cirrhosis so susceptible?

Who will benefit from reading this chapter?
-
Any Patient with Cirrhosis
-
Caregivers
-
Family & Friends
-
Physicians & Other Healthcare Practitioners
This chapter covers the following topics:
-
What foods to avoid eating? Which foods are good for the liver?
-
BMI Calculator (Body Mass Index)
-
Daily calorie intake - what is it and why it is important
-
Important nutrients: protein & sodium
-
How and why it's important to track body weight

Who will benefit from this chapter?
-
Any Patient with Cirrhosis
-
Caregivers
-
Family & Friends
-
Physicians & Other Healthcare Practitioners
This chapter includes the following topics:
-
How to manage fatigue, cooking, and eating
-
How to cope when getting full after just a few bites
-
Smart tips for stretching the food budget
-
How to stick to a regular eating schedule
Who will benefit from reading this chapter?
-
Any Patient with Cirrhosis
-
Anyone who prepares food for person living with cirrhosis
-
Caregivers
-
Family & Friends
-
Physicians & Other Healthcare Practitioners
This chapter includes liver-friendly recipes that are:
-
Nutritious
-
Easy to prepare & use inexpensive ingredients
-
Modifiable to accommodate dietary restrictions, tastes & preferences
-
Weight maintenance & weight loss friendly
-
Suitable for those with & without cirrhosis
Some recipe examples are:
-
Baked Chicken Dinner
-
Salmon Salad
-
Homemade Banana Muffins - YUM!
-
Black Bean Soup
Who will benefit from reading this chapter?
-
Anyone cooking for a Patient with Cirrhosis
-
Any Patient with Cirrhosis
-
Family & Friends
-
Physicians & Other Healthcare Practitioners
-
Anyone looking for easy-to-make, nutritious & delicious recipes!
This chapter includes topics about:
-
When are meal supplements useful?
-
Common meal supplement drinks
-
Which supplement drinks are best for which health conditions

Who will benefit from this chapter?
-
Any Patient with Cirrhosis with a poor appetite or needing snack ideas
-
Caregivers
-
Family & Friends
-
Physicians & Other Healthcare Practitioners
This chapter includes sections on:
-
Diet priorities for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
-
Protein intake - it's a priority!
-
Tips for reaching daily protein targets
-
Eating to help the liver & lose weight at the same time - Help?
Who will benefit from this chapter?
-
All Patients with NAFLD, NASH, or cirrhosis caused by NAFLD or NASH
-
Caregivers
-
Family & Friends
-
Physicians & Other Healthcare Practitioners

This chapter includes topics about:
-
What meals and snacks to expect
-
I can't follow my usual eating schedule - Help?
-
What is a "nasogastric (NG) feed"
-
Why an NG may be prescribed
Who will benefit from reading this chapter?
-
Any Patient with Cirrhosis who is being admitted to the hospital
-
Caregivers
-
Family & Friends
-
Physicians & Other Healthcare Practitioners
Eating well in hospital
Useful Links
References:
The information on this page was adapted (with permission) from the references below, by the Cirrhosis Care Alberta project team (physicians, nurse practitioners, registered nurses, registered dietitians, physiotherapists, pharmacists, and patient advisors).
This information is not intended to replace advice from your healthcare team. They know your medical situation best. Always follow your healthcare team’s advice.
References: